2D and 3D Geometry Formulas
| Shape | Formula |
|---|---|
Input: Sides Lengths of Right Triangle 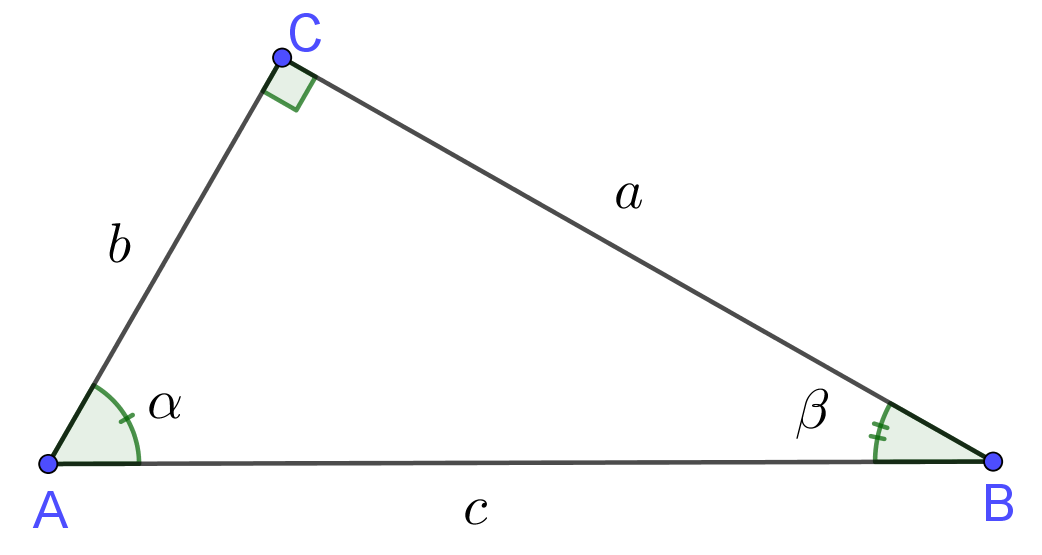
|
Pythagorean Theorem Formula
$c^2 = a^2 + b^2$
|
Input: Two points $A(x_A,y_A)$ and $B(x_B,y_B)$ 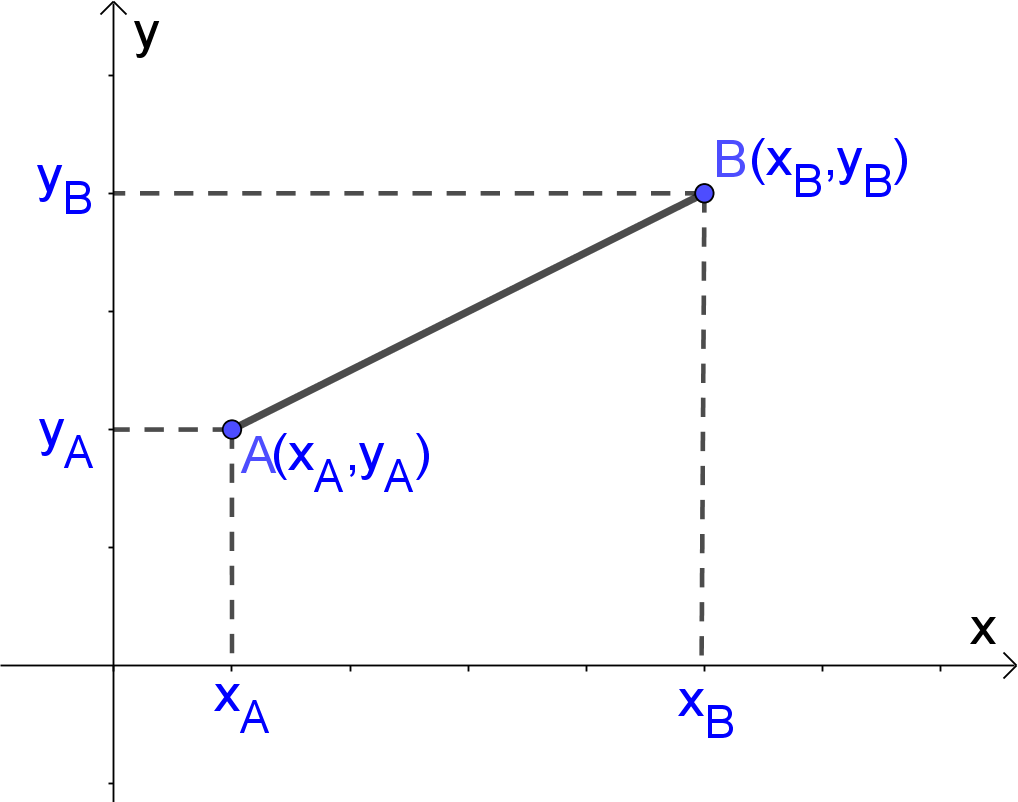
|
Length Between Two Points
${AB}=d(A,B)=\sqrt{(x_B-x_A)^2+(y_B-y_A)^2}$
|
Input: Two points $A(x_A,y_A)$ and $B(x_B,y_B)$ 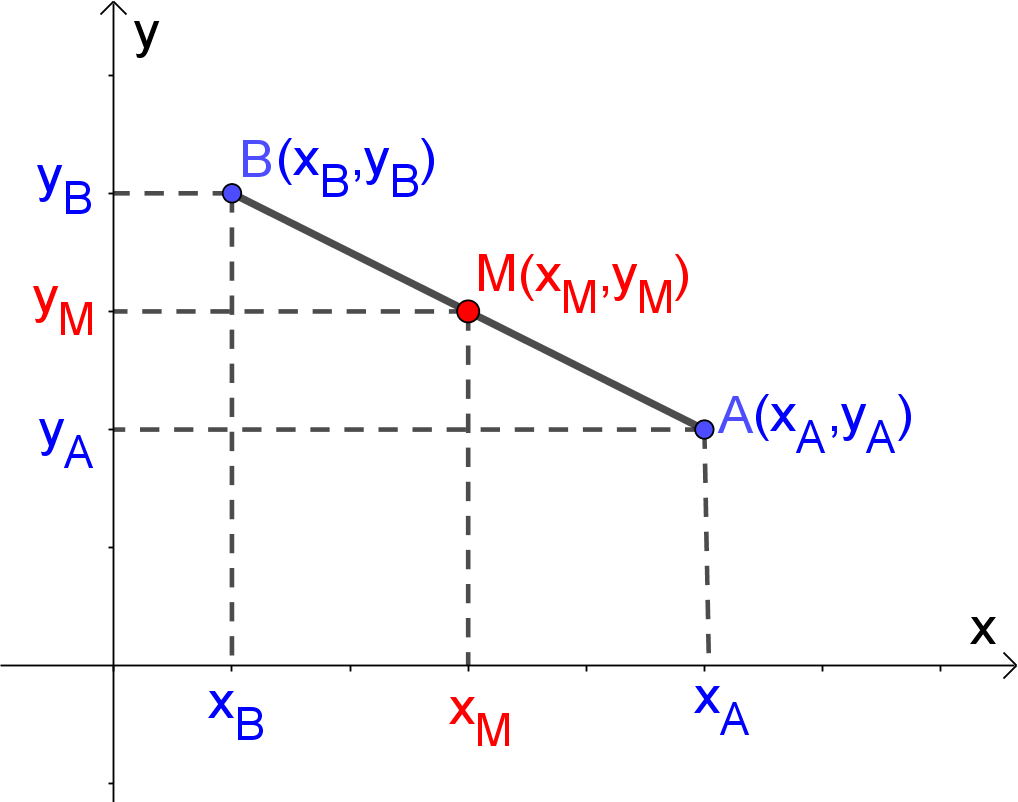
|
Midpoint of Line Segment
$M\Big(\frac{x_A+x_B}{2},\frac{y_A+y_B}{2}\Big)$
|
Input: Three non-collinear points $A(x_A,y_A), B(x_B,y_B)$ and $C(x_C, y_C)$ 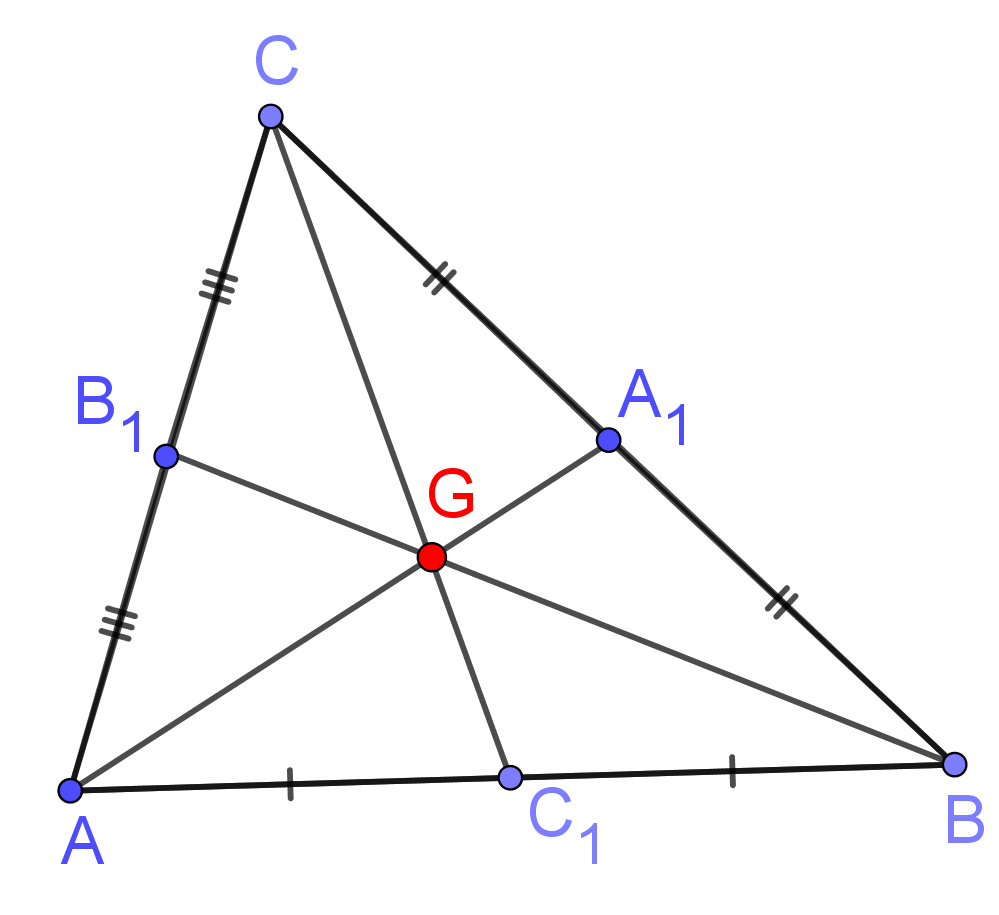
|
Centroid Triangle
$C\Big(\frac{x_A+x_B+x_C}{3},\frac{y_A+y_B+y_C}{3}\Big)$
|
Input: Point $A(x_A,y_A)$ and line $(p):Ax+By+C=0$ 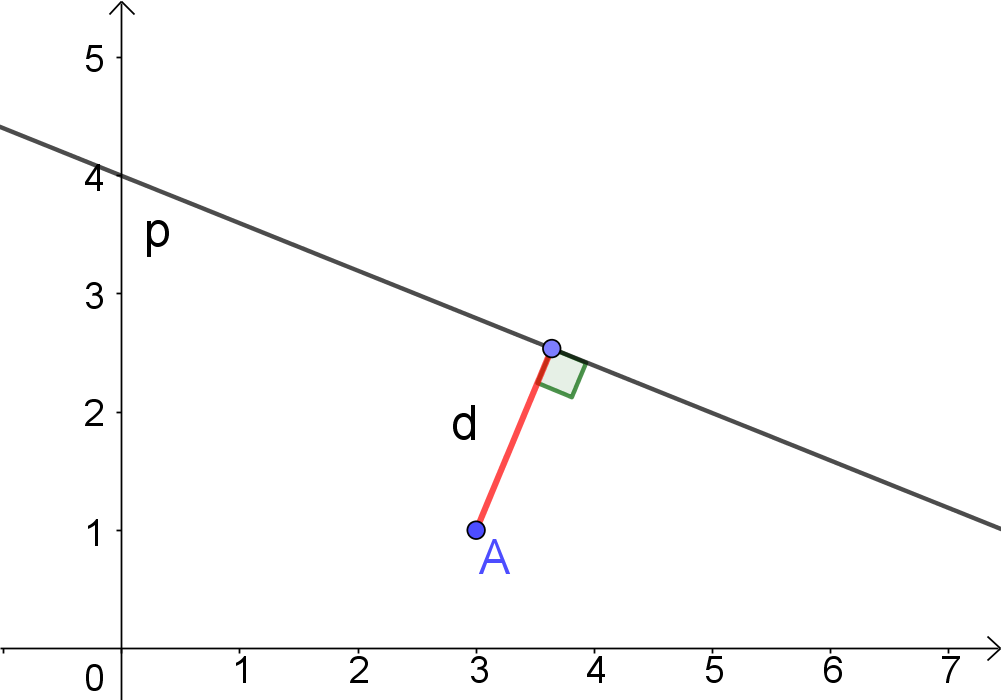
|
Perpendicular Length
$d(A,p)=\Big|\frac{Ax_A+By_B+C}{\sqrt{A^2+B^2}}\Big|$
|
Input: Point $A(x_A,y_A)$ and slope $m$ 
|
Point Slope Form
$y-y_A=m(x-x_A)$
|
Input: Slope $m$ and intercept $b$ 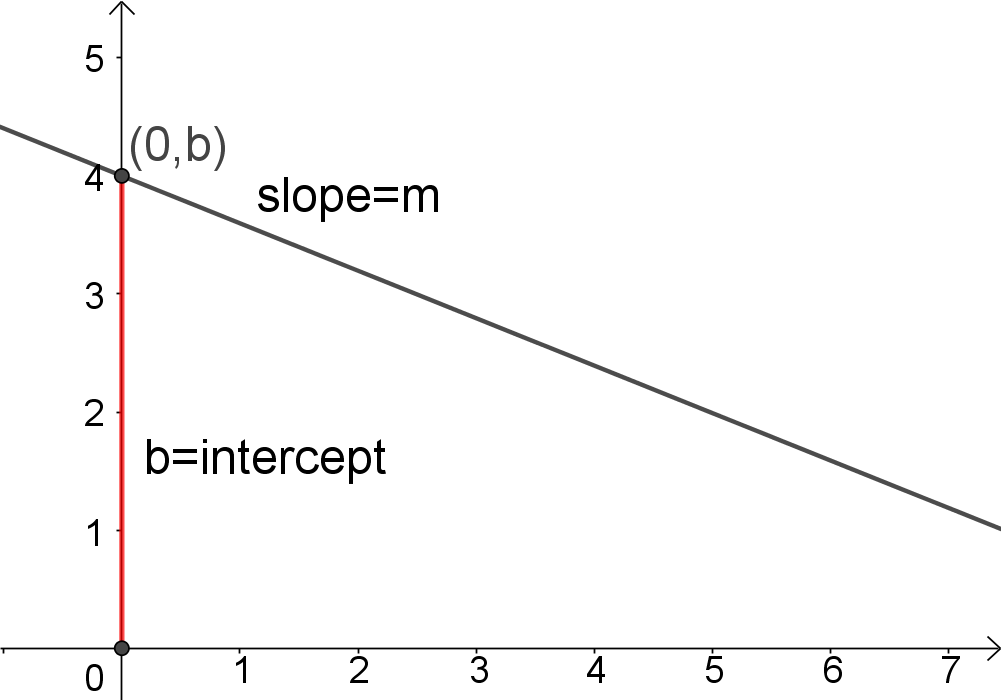
|
Slope Intercept Form
$y=mx+b$
|
Input: Two points $A(x_A,y_A)$ and $B(x_B,y_B)$ 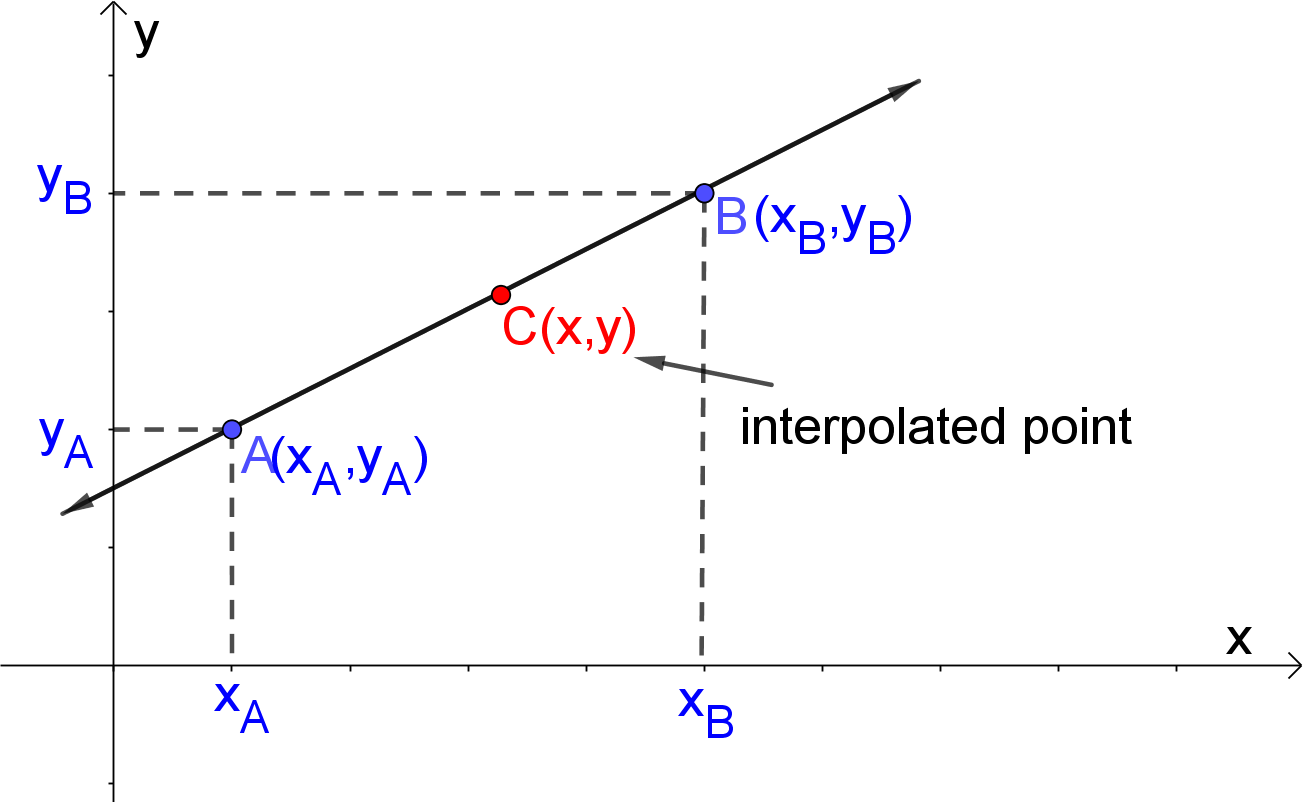
|
Linear Interpolation
$x_C=\frac{x_B(y_C-y_A)+x_A(y_B-y_C)}{y_B-y_A}$
$y_C=\frac{y_B(x_C-x_A)+y_A(x_B-x_C)}{x_B-x_A}$ |
Input: Three non-collinear points$A(x_A,y_A), B(x_B,y_B)$\ and $C(x_C, y_C)$ 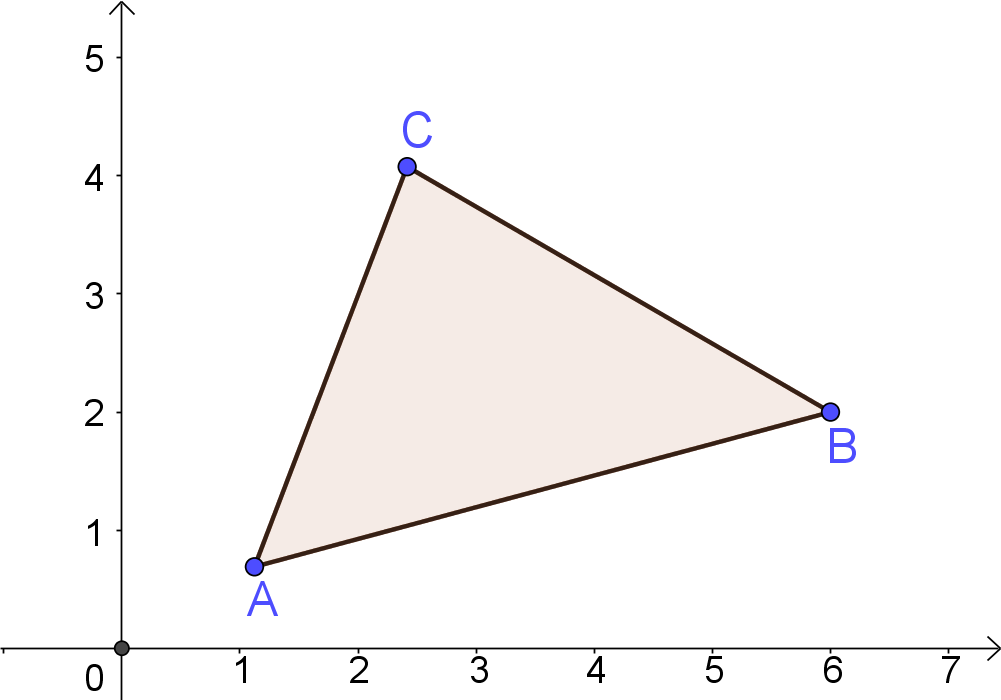
|
Area of Triangle
$A=\frac 12[x_A(y_B-y_C)+x_B(y_C-y_A)+x_C(y_A-y_B)]$
|
Input: Radius $r$ or Diameter $D$ 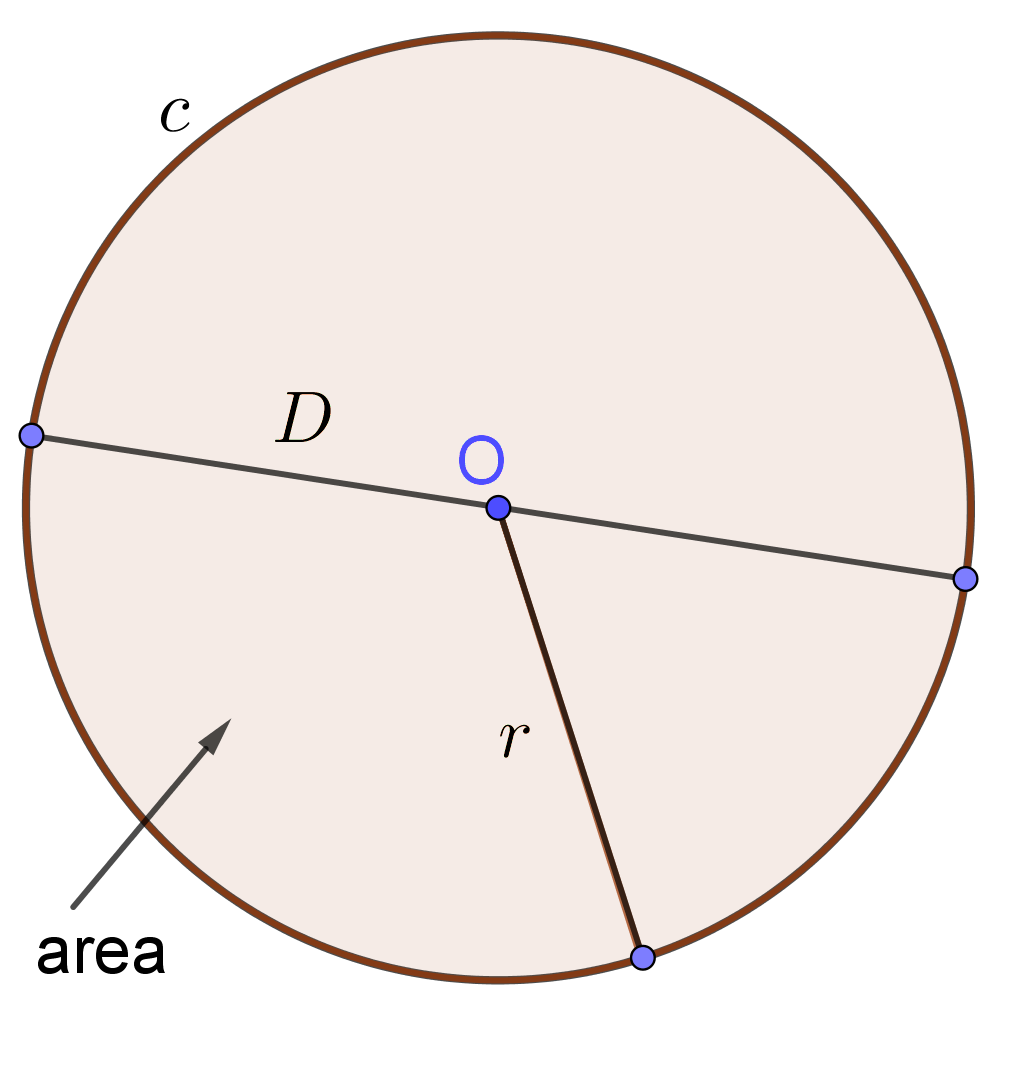
|
Circle Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=r^2\pi$
$\mbox{Diameter}\; D=2r$ $\mbox{Circumference}=2r\pi$ |
Input: Radius $r$ and central angle $\alpha$ in degrees of circular sector 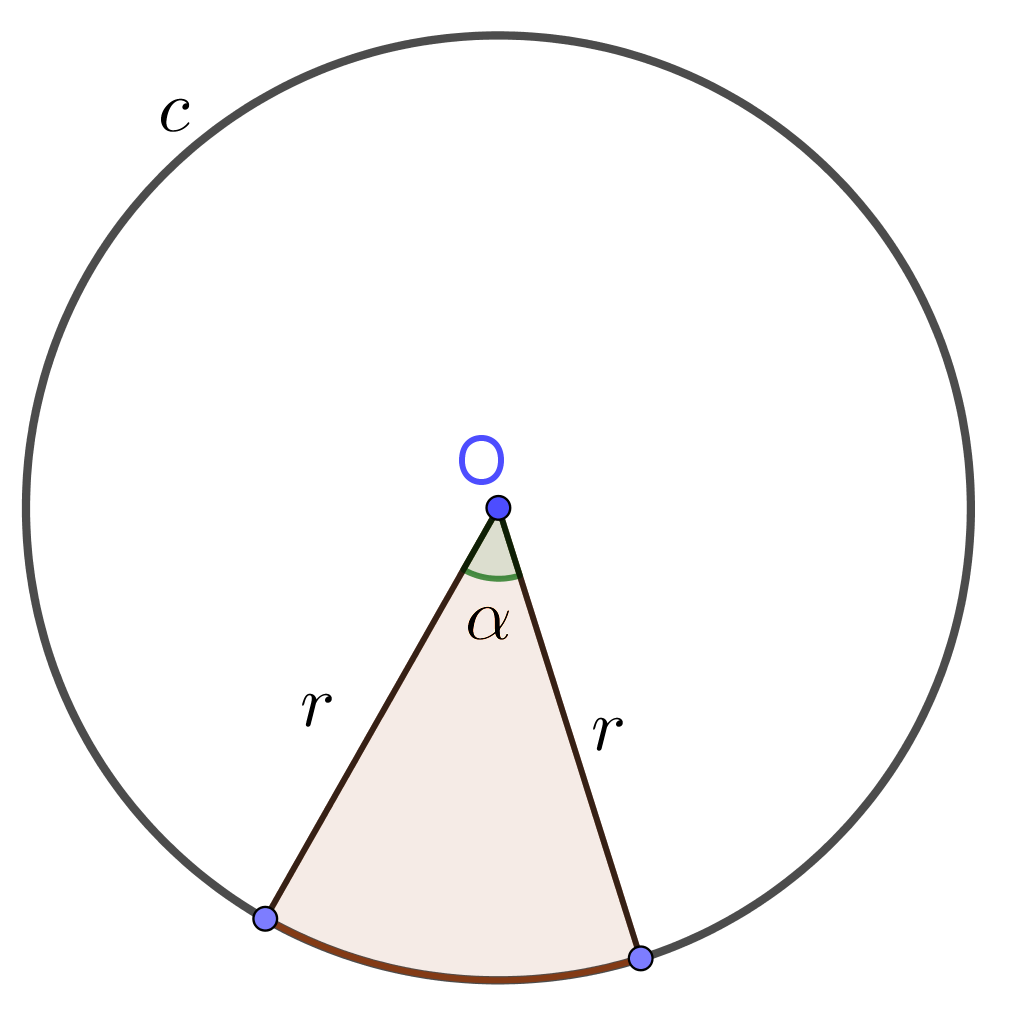
|
Circular Sector Formula
$\mbox{Area}=\frac{\pi r^2\alpha}{360^o}$
|
Input: Major radius $a$ and minor radius $ b $ of Ellipse 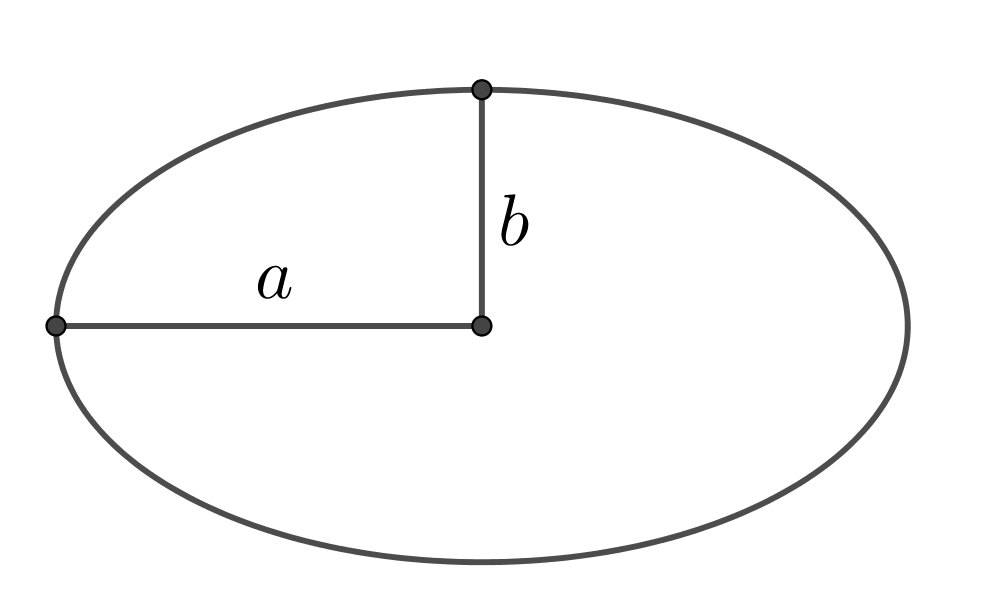
|
Ellipse Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=\pi ab$
$\mbox{Perimeter}=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{a^2+b^2}{2}}$ |
Input: Side $a$ or diagonal $d$ of Square 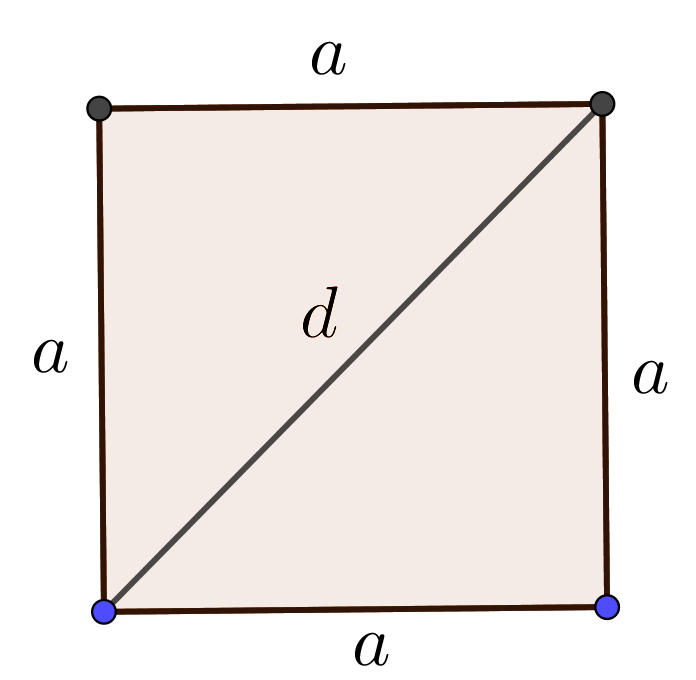
|
Square Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=a^2$
$\mbox{Perimeter}=4a$ $\mbox{Diagonal}\;d=\sqrt{2}a$ |
Input: Length $l$ and width $w$ of Rectangle 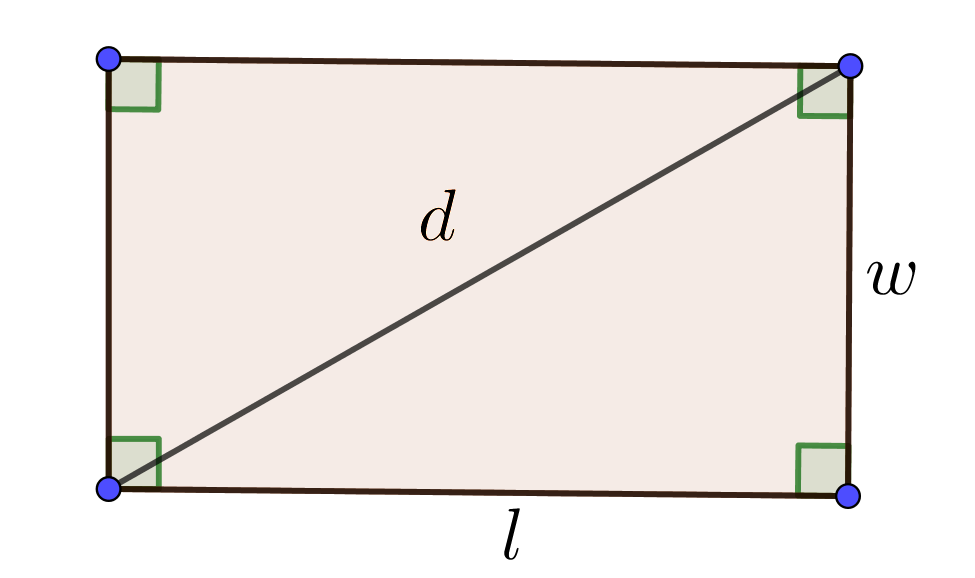
|
Rectangle Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=\mbox{length}\times\mbox{width}$=lw
$\mbox{Perimeter}=2l+2w$ $\mbox{Diagonal}\;d=\sqrt{l^2+w^2}$ |
Input: Sides $a,b$ and $c$ of Triangle 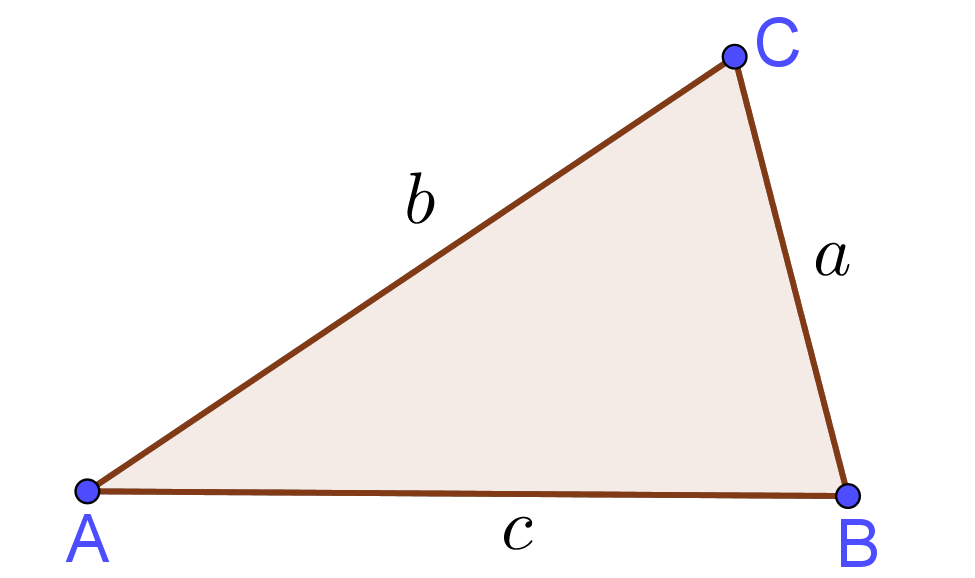
|
Heron's Triangle Formula
$\mbox{semiperimeter}\;s=\frac{a+b+c}{2}$
$\mbox{Area}=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$ |
Input: Base $c$ and its height $h$ of Triangle 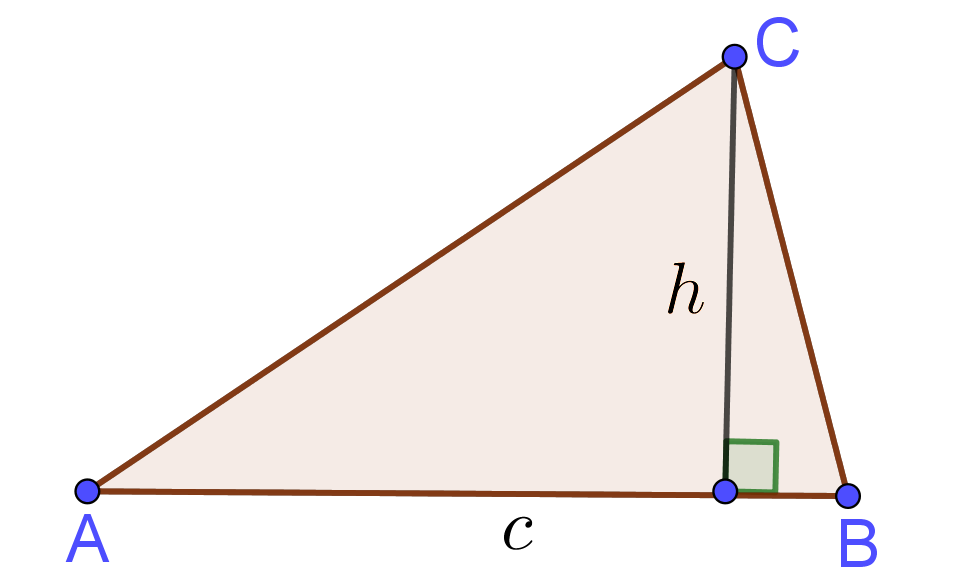
|
Triangle Formula
$\mbox{Area}=\frac{ch}{2}$
|
Input: Bases $a$ and $b$ and height $h$ of Trapezoid 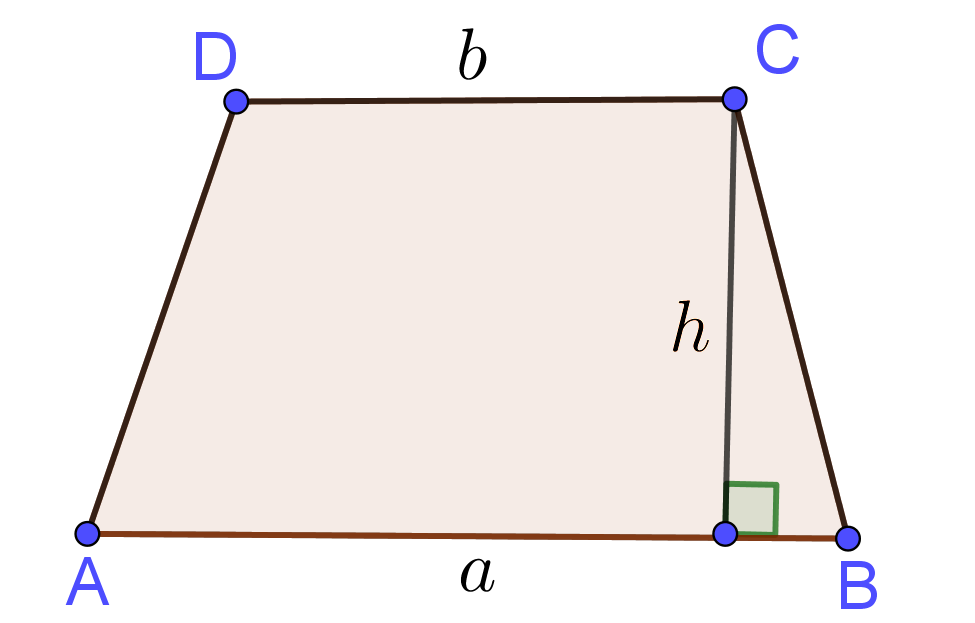
|
Trapezoid Formula
$\mbox{Area}=\frac{a+b}{2}h$
|
Input: Side $a$ and interior angle $\alpha$ or diagonals $d_1$ and $d_2$ of Rhombus 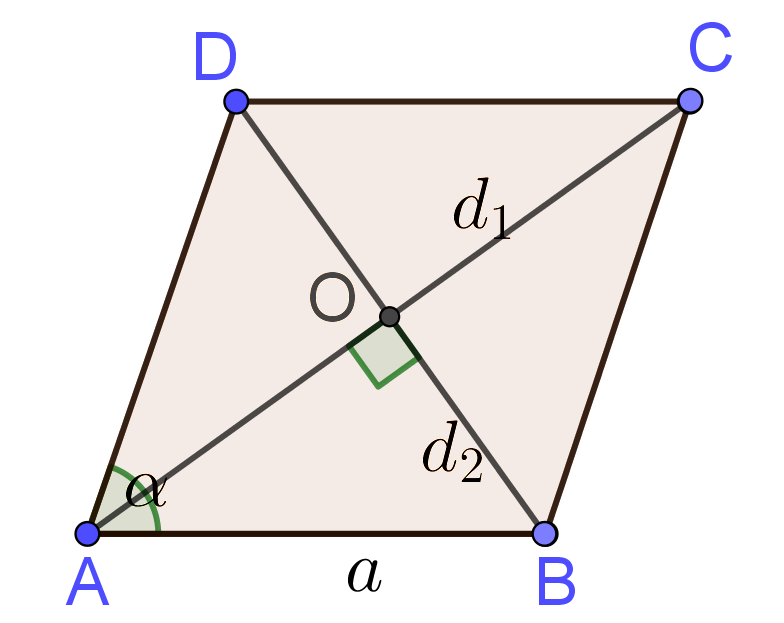
|
Rhombus Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=a^2\sin\alpha$
$\mbox{Area (diagonal method)}=\frac{d_1d_2}{2}$ $\mbox{Perimeter}=4a$ |
Input: Base $a$ and its height $h$ of Parallelogram 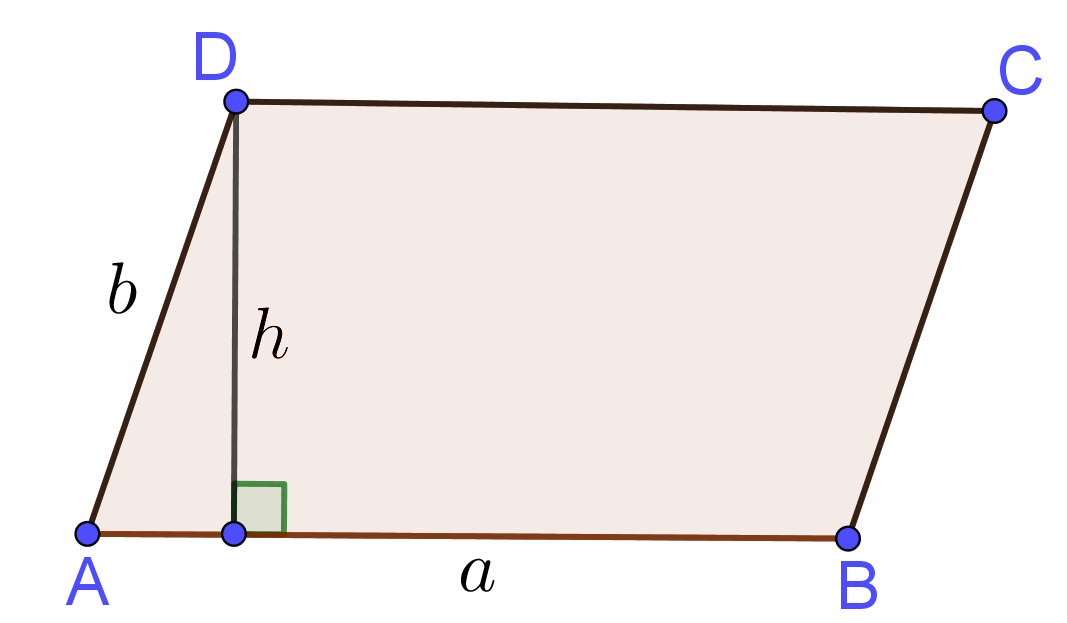
|
Parallelogram Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=\mbox{base}\times\mbox{height}={ah}$
|
Input: Radius $r$ or diameter $D$ of sphere 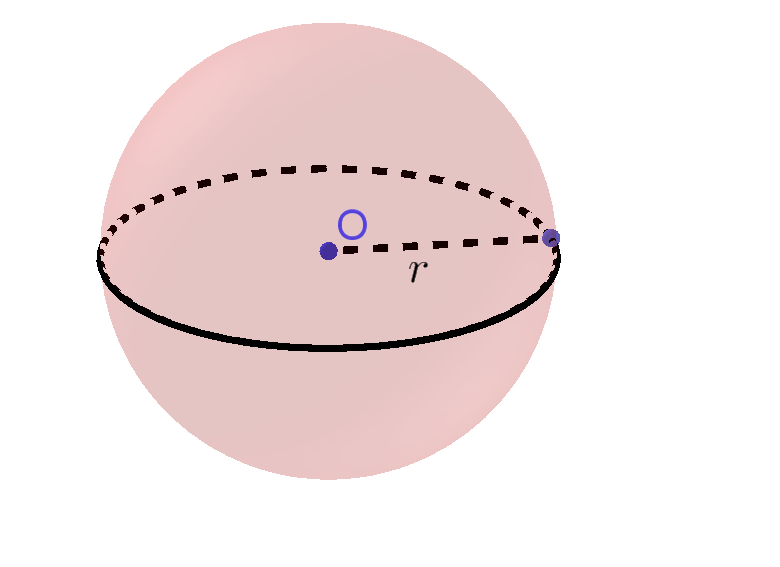
|
Sphere Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=4\pi r^2=\pi D^2$
$\mbox{Volume}=\frac 43\pi r^3=\frac 16\pi D^3$ |
Input: Radius $r$ of Hemisphere 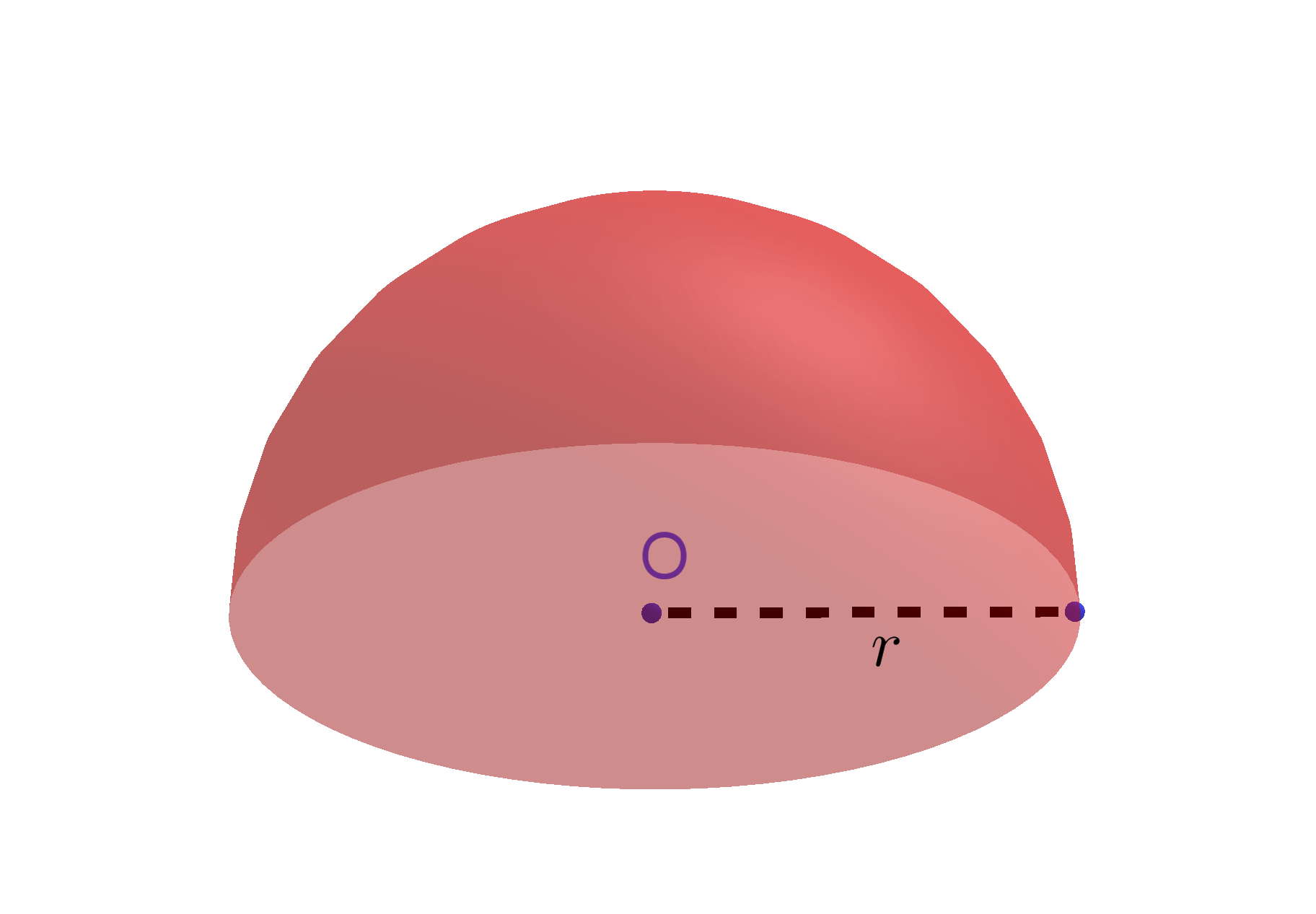
|
Hemisphere Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=3\pi r^2$
$\mbox{Volume}=\frac 23\pi r^3$ |
Input: Base radius $r$ and height $h$ of Cone 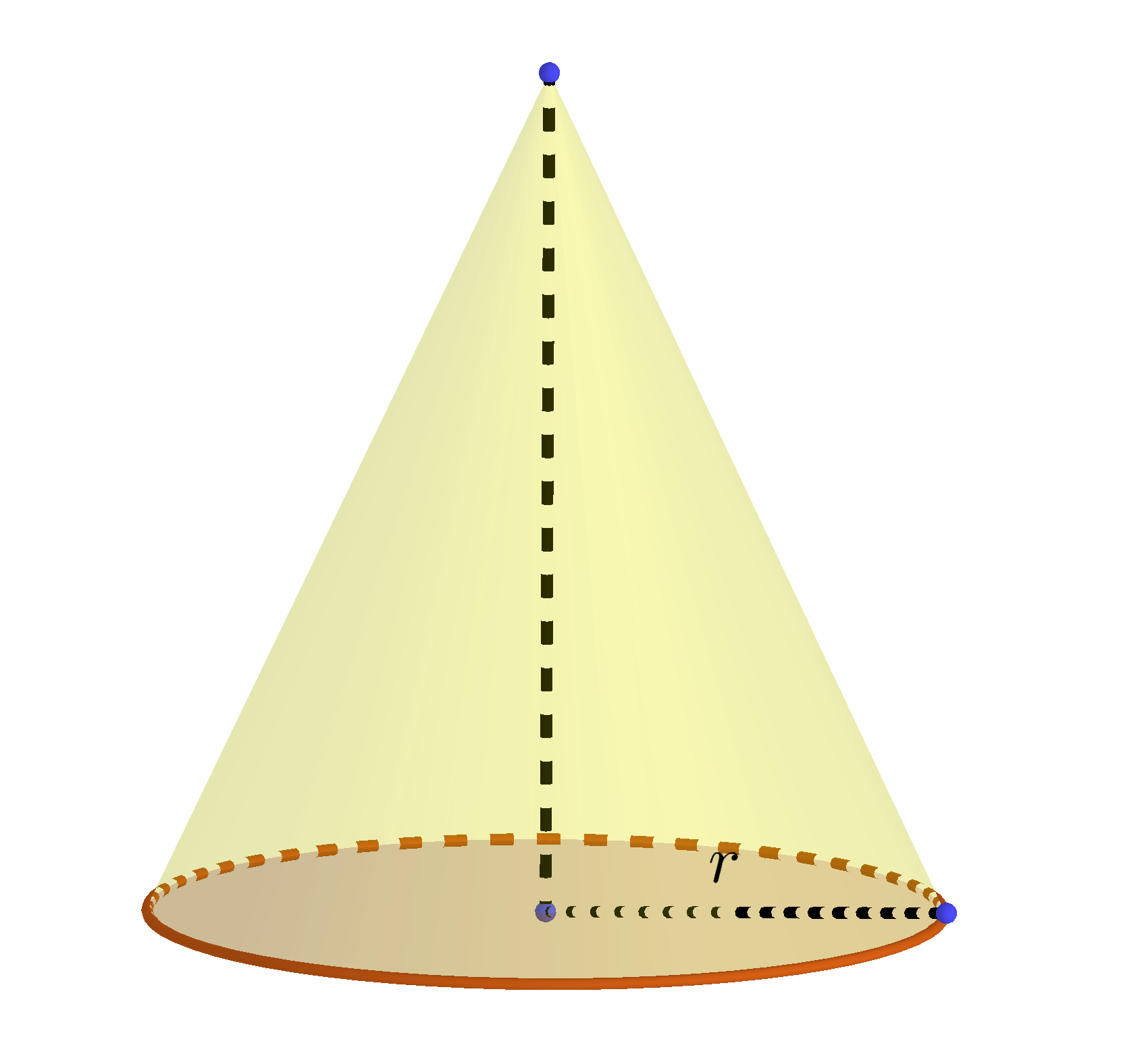
|
Cone Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=\mbox{side area}+\mbox{base area}=\pi r(\sqrt{r^2+h^2}+r)$
$\mbox{Volume}=\frac 13\pi r^2h$ $\mbox{Slant Height}=\sqrt{r^2+h^2}$ |
Input: Base radius $r$ and height $h$ of Cylinder 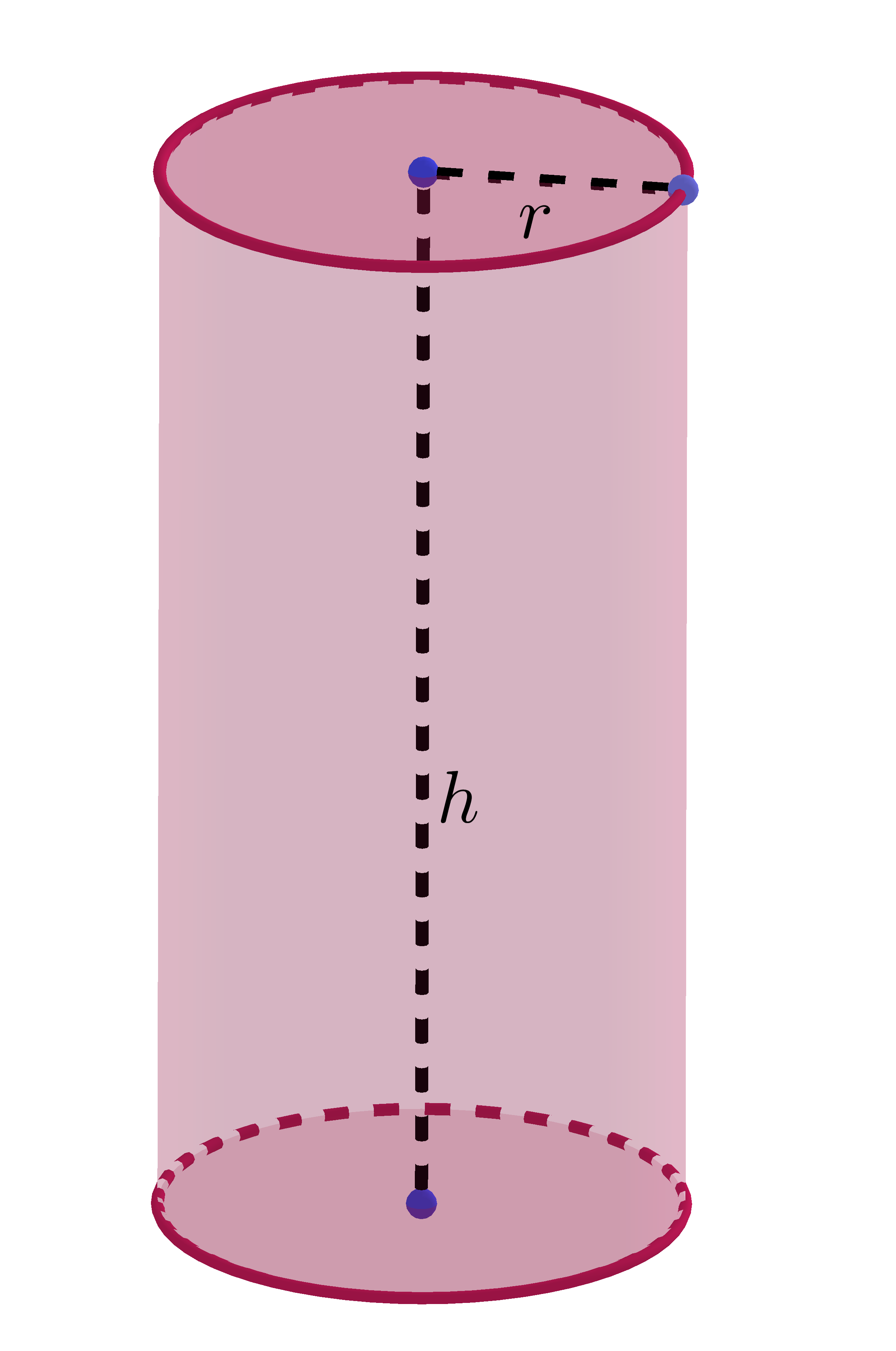
|
Cylinder Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=2\pi r(r+h)$
$\mbox{Volume}=\pi r^2h$ $\mbox{Base surface area}=\pi r^2$ $\mbox{Lateral surface area}=2\pi rh$ |
Input: Side $a$ of Cube 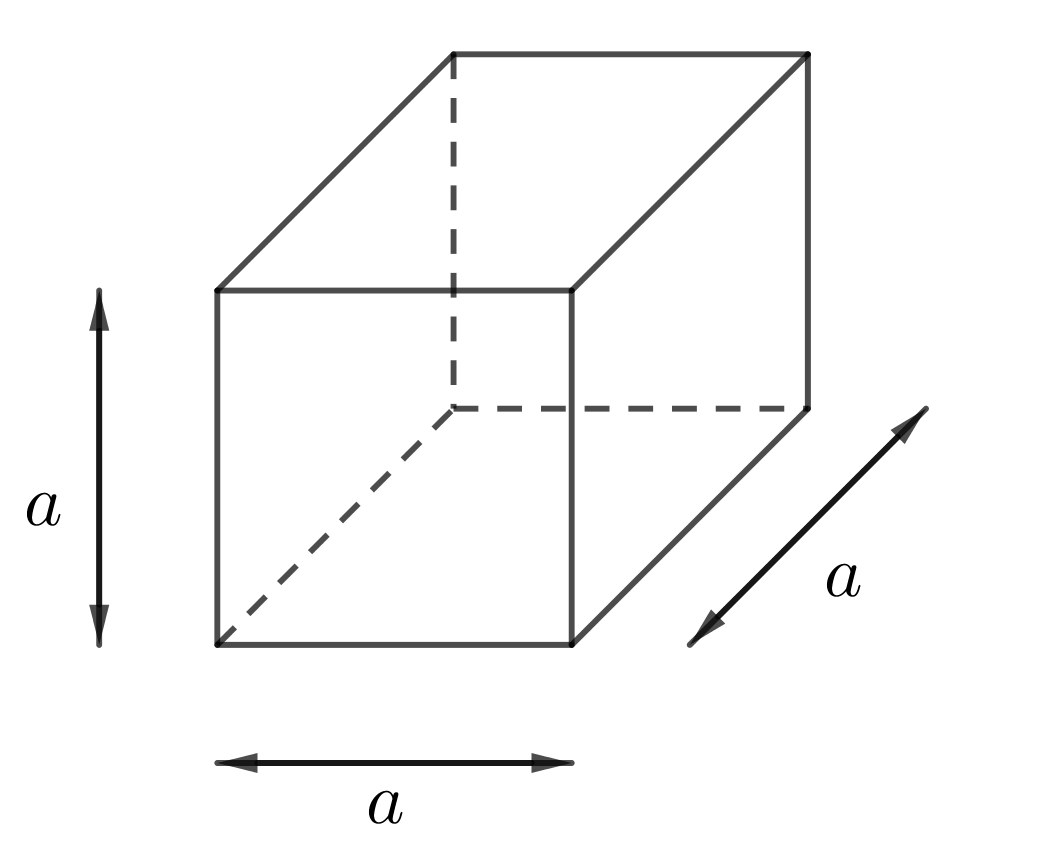
|
Cube Formulas
$\mbox{Area}=6a^2$
$\mbox{Volume}=a^3$ |
Input: Base side and height of Pyramid 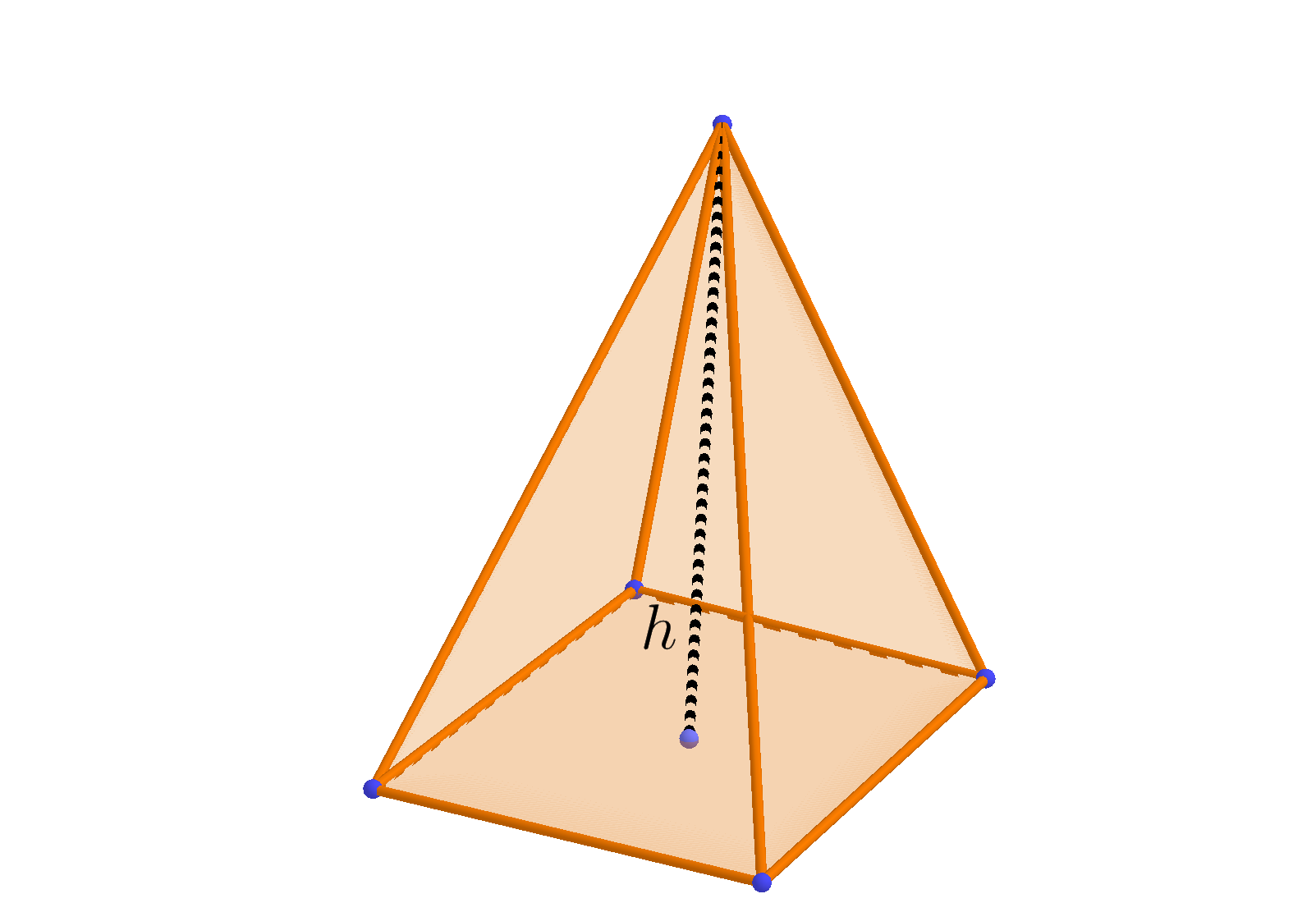
|
Pyramid Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=\mbox{base area}+\frac 12\mbox{perimeter base}\times \mbox{slant height}$
$\mbox{Volume}=\frac 13\mbox{base area}\times\mbox{height}$ |
Input: Outer radius $R$, inner radius length $r$ and height $h$ of a Pipe 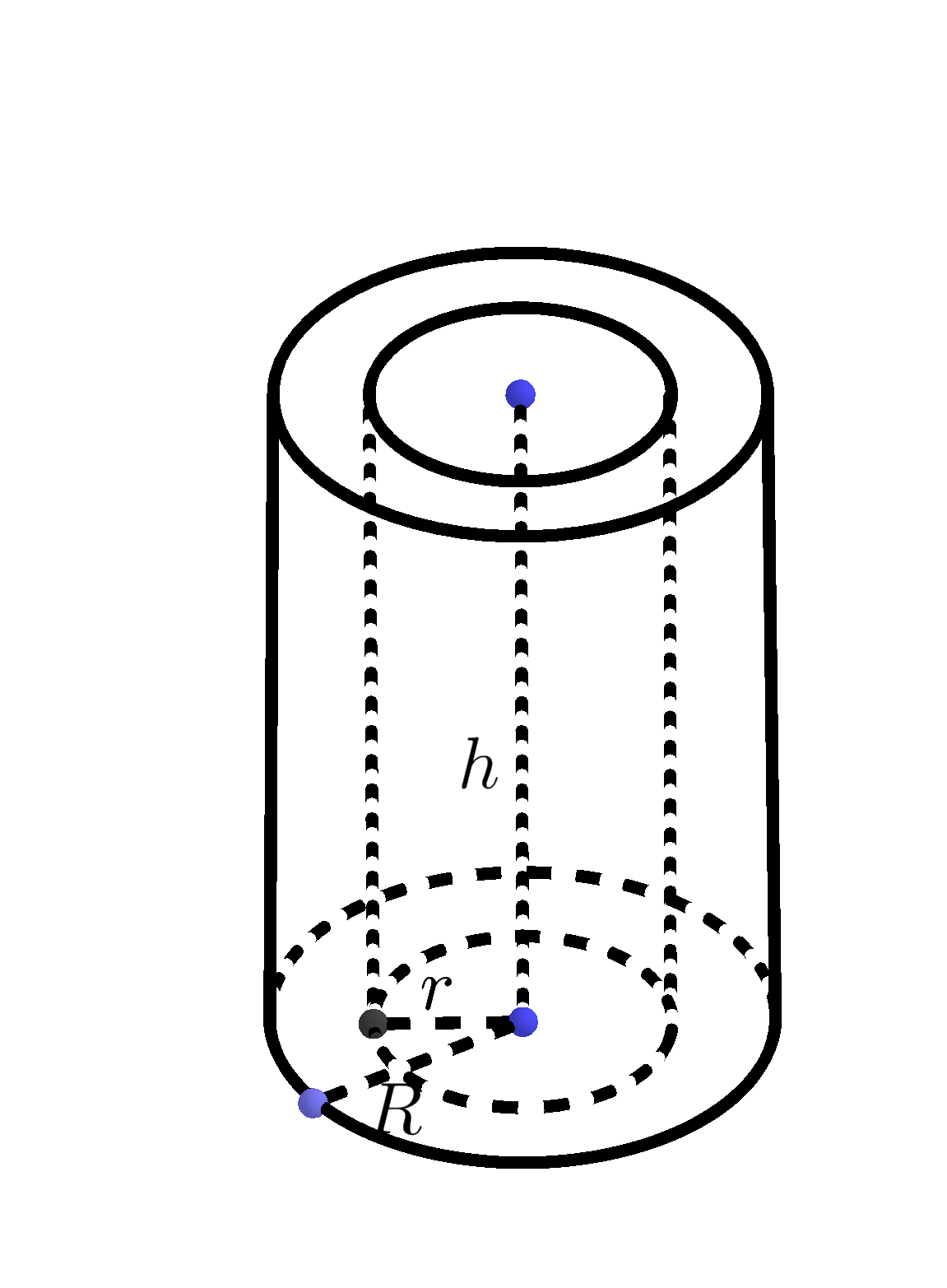
|
Pipe Formulas
$\mbox{Volume}=\pi(R^2-r^2) h$
|
Input: Base radius $r$ and height $h$ of Cylindrical Silo 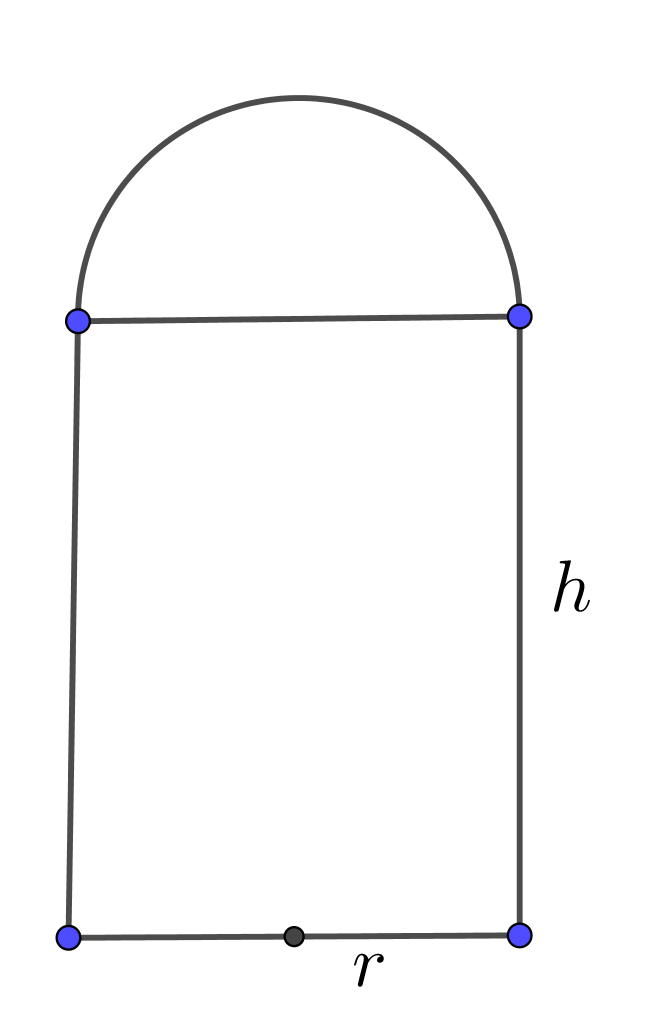
|
Cylindrical Silo Formulas
$\mbox{Volume}=\pi r^2h+\frac{2\pi r^3}3$
|
Input: Length $l$, width $w$ and height $h$ of Cuboid 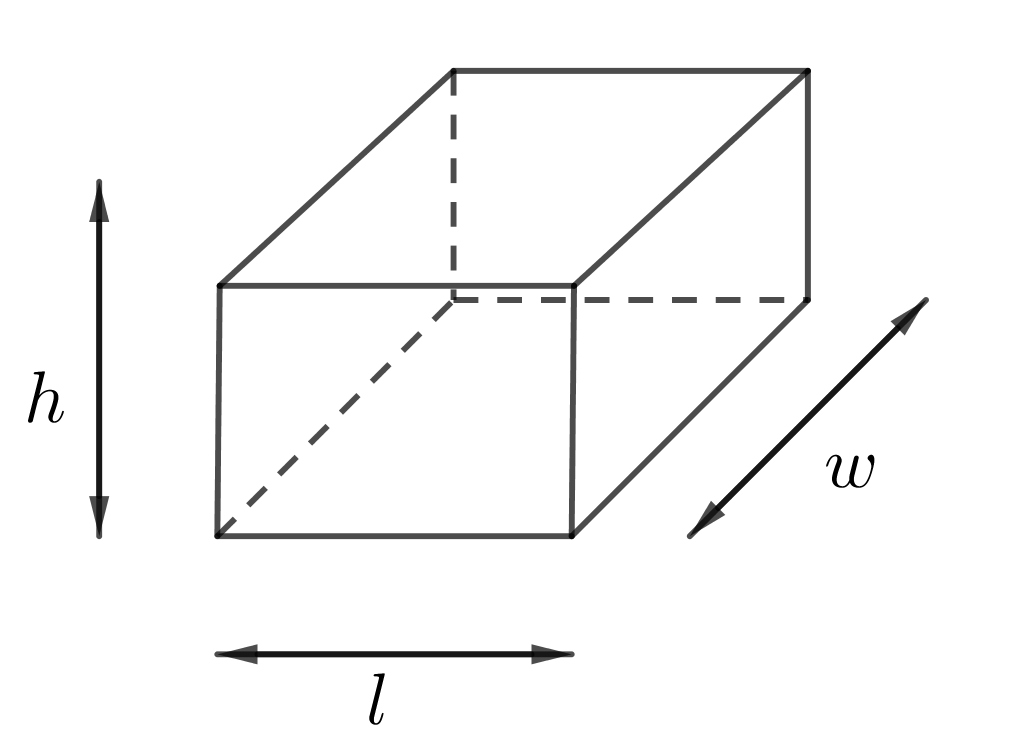
|
Rectangular Cuboid Formulas
$\mbox{Surface Area}=2(lw+hl+hw)$
$\mbox{Volume}=lwh$ $\mbox{Diagonal}=\sqrt{l^2+w^2+h^2}$ $\mbox{Length around edges}=4(l+w+h)$ |
Input: Middle radius $D$ top or bottom radius $d$ and height $h$ of Barrel 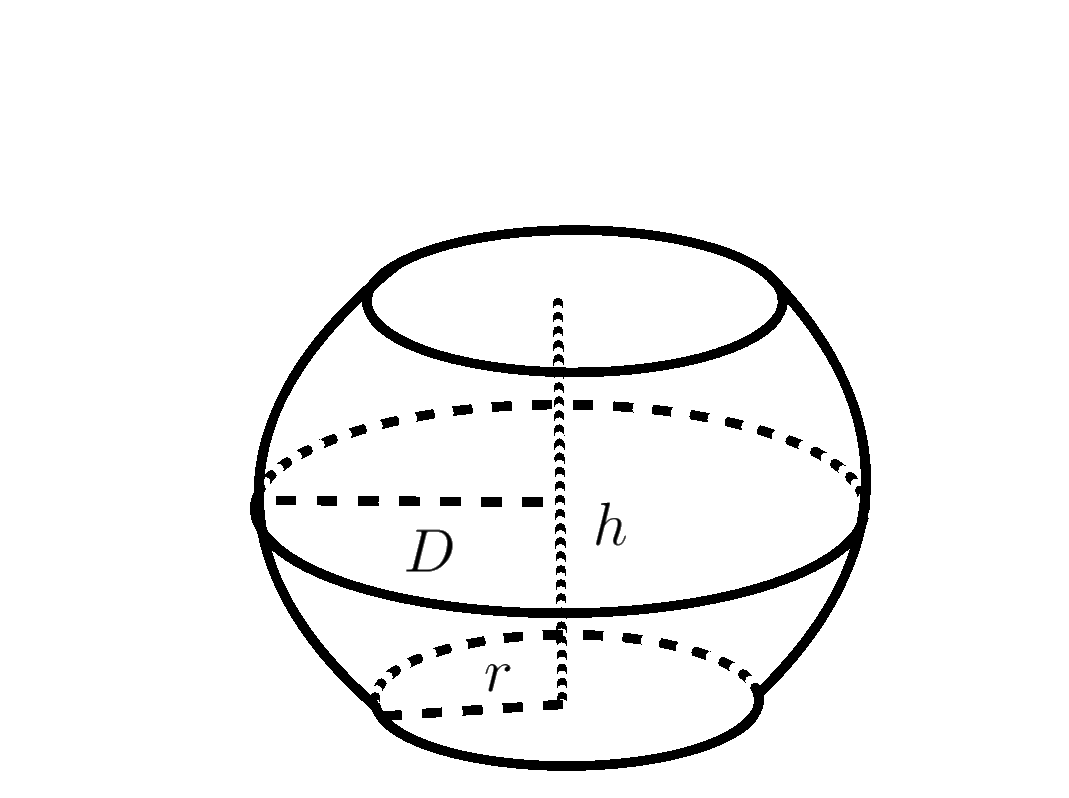
|
Barrel Formulas
$\mbox{Volume}=\frac{\pi h}{12} (2D^2+d^2)$
|
Geometry Formulas Reference
Geometry formulas reference is the collection equations for the study of 2 or 3 dimensional (2d or 3d) geometric shapes. This formulas cheatsheet deals with points, lines, planes, curves, angles, length, area, perimeter, volume, surfaces of different geometric shapes. This formulas cheatsheet is useful to know what are all the basic components used in the each functions of geometric functions.
